Contemporary text-to-speech (TTS) systems are achieving increasingly impressive humanlike voice generation performance in terms of intelligibility and naturalness. A lack of diverse speech data however makes it challenging to faithfully capture the many different speaker identities, prosodies and styles that can present in human speech.
In the new paper NaturalSpeech 2: Latent Diffusion Models are Natural and Zero-Shot Speech and Singing Synthesizers, a Microsoft Research Asia and Microsoft Azure Speech team introduces NaturalSpeech 2, a TTS system with latent diffusion models for natural and strong zero-shot voice synthesis that captures expressive prosodies and speech styles such as singing with superior robustness.

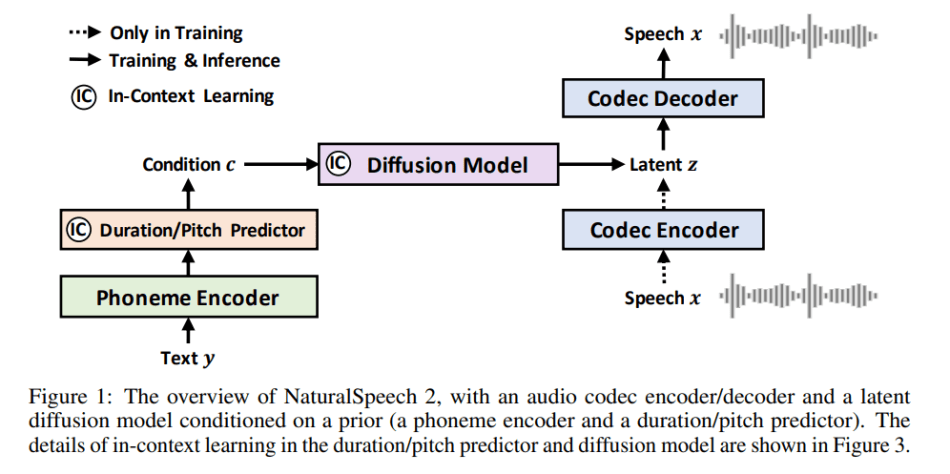
The team first trains a neural audio codec, which transforms speech waveforms into a sequence of latent vectors via a codec encoder and then reconstructs the speech waveform from these latent vectors via a codec decoder. They then employ a diffusion model to generate these latent vectors based on prior vectors obtained from a phoneme encoder, a duration predictor, and a pitch predictor.
The team’s approach introduces a number of design improvements compared to conventional TTS systems. Firstly, it uses continuous vectors instead of discrete tokens, thus reducing the sequence length while increasing information for fine-grained speech reconstruction. Secondly, a diffusion model replaces the conventional autoregressive model to enable better learning of complex distributions of continuous vectors. Thirdly, novel speech prompting mechanisms enable in-context learning in the diffusion model and pitch predictor. These changes make NaturalSpeech 2 more stable and robust.

In their empirical study, the team compared NaturalSpeech 2 with a YourTTS baseline on LibriSpeech and VCTK corpora. In the experiments, NaturalSpeech 2 consistently outperformed YourTTS, better capturing speakers’ prosody, robustness and voice quality in a zero-shot setting; and performing natural zero-shot singing synthesis from only a brief speech prompt.
Overall, this work demonstrates NaturalSpeech 2’s power and potential in terms of expressiveness, robustness, fidelity, and zero-shot ability. The team plans to explore additional strategies to further speed up the diffusion model and enable more powerful mixed speaking/singing capabilities.
Audio samples are available on the project’s GitHub. The paper NaturalSpeech 2: Latent Diffusion Models are Natural and Zero-Shot Speech and Singing Synthesizers is on arXiv.
Author: Hecate He | Editor: Michael Sarazen

We know you don’t want to miss any news or research breakthroughs. Subscribe to our popular newsletter Synced Global AI Weekly to get weekly AI updates.

0 comments on “Microsoft’s NaturalSpeech 2 Outperforms Previous TTS Systems in Zero-Shot Speech and Singing Synthesis”